How Reliable Are At-Home Hearing Tests?
Hearing is so essential to how we engage with the people and activities
By: admin | May 24, 2022
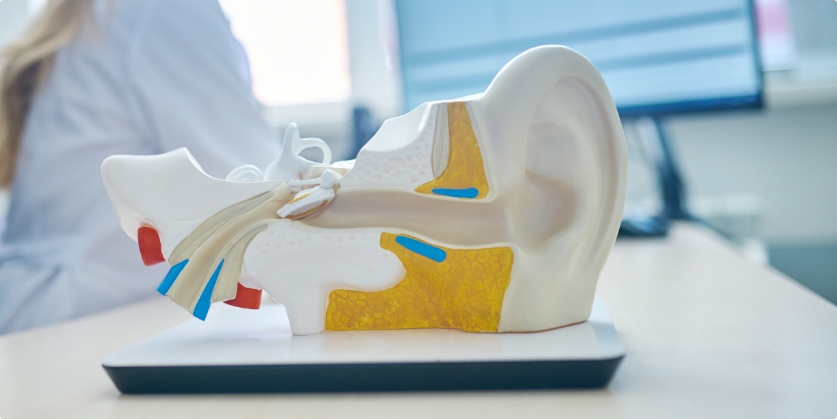
The stapes, or the stirrup bone, is found in the middle ear and is the smallest bone in the entire human body. It’s one of three tiny bones called the auditory ossicles that are suspended by three ligaments and form a chain across the length of the middle ear. The stirrup, anvil, and hammer bones all work together to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled cochlea, which transforms them into electrical signals. And together, these tiny bones are only about the size of a penny! Serious infections or head injuries can damage the ossicles, and if they are not functioning properly, you may suffer from moderate-to-severe hearing loss.
The hardest bone in the human body is the temporal bone, which protects our inner ears. In addition to providing structural support for the skill, the temporal bone surrounds the middle and inner portions of the ear. The temporal bone attaches to the joint of the jawbone, so if you grind your teeth or are an excessive gum chewer, you may have experienced pain or soreness in this area. The temporal bone is made of porous material, so untreated ear infections can spread through it in the interior of the skull. Make sure to see a medical professional if you suspect you have an ear infection to prevent serious damage.
Our ears produce cerumen, or earwax, which is secreted by the body as the middle ear’s natural defense against dirt, dust, and other environmental irritants, and even protect us against fungal or bacterial infections. Ears can clean themselves thanks to the pores and cilia, thousands of tiny hairs. Earwax is made up of dead skin cells, hair, and substances secreted by glands in our ear canal, and it moves out of the ear at the same rate as our fingernails grow (approximately 1.3 inches a year). Normal activities like chewing or other jaw movement contributes to this process by dislodging any debris attached to the inner walls of the ear canal, which is then expelled with the earwax. While it is an important part of our body’s defense mechanisms, excessive earwax can press up against our sensitive ear drums or block our ear canals. This can be painful! Don’t try to remove excess or impacted wax at home. Inserting cotton swabs, fingers, or other objects into your ears can move debris or irritants farther down the or damage the thin layer of skin that lines your ear canal, which can also result in an infection. See your doctor or a hearing professional for a safe, professional removal of excess earwax.
In medieval times, earwax (and middle ear fluid) and other bodily fluids were used to prepare pigments that were used by scribes to illustrate early illuminated manuscripts! Earwax has even been used by anthropologists to study the migratory patterns of early humans.
Click here to book an appointment with our specialist now!
Why are some noises so unpleasant to the human ear? A study published in the Journal of Neuroscience by the University of Newcastle subjected volunteers to different sounds and monitored the responses. According to brain scans and other data obtained, there is an interaction between the region of the brain that processes sound and the amygdala, which is involved in the development of negative emotions. This relationship between the emotional and auditory areas of the brain explains why some noises make us want to jump out of our skin. The following sounds occur in the frequency range between 2000 and 5000 hertz, which is the range in which human ears are most sensitive to sound. The list includes:
The study also identified the most PLEASANT sound for the human ear. Can you guess? It’s the sound produced by boiling water! Scientists are using the results of this study in research for curing emotional disorders, migraines, and any other disease that causes a greater sensitivity of the cerebral cortex to noise.
Some hearing problems can be mitigated or prevented entirely by your diet. According to some studies, a diet rich in fruits and veggies, foods that contain potassium, magnesium, zinc, and folic acid, can lower the risk of hearing loss by up to 30%. Some leafy greens like lettuce and spinach can help prevent hearing issues associated to exposure to noise. Foods with a high count of Omega 3 fatty acids, such as fish like salmon or tuna, can help strengthen the blood vessels in our inner ears. A vitamin D deficiency can cause bones to become weak and lose function, and that can affect the tiny bones in our inner ears as well. This can lead to hearing loss. Fill your plate with colors! Carrots, peppers, kiwi, broccoli, and melon can all contribute to your hearing health. Human bones don’t reach maximum density until we are about 30 years old, so a healthy diet is especially important for children and young adults.
You may only think about your earlobes when you are shopping for jewelry, but they are a fascinating link in the chain of human evolution! Human beings present with only two types of earlobes, attached or detached, and your lobes are determined entirely by genetics. Scientists aren’t sure yet what the function of earlobes is, but due to the large number of blood vessels contained within them, some posit that it may help with blood flow.
Healthy ears are essential to keep you on an even keel. If you have ever had an ear infection, you may have suffered from balance problems, dizziness, nausea, or even vertigo. More than 20,000 hair cells move through fluid deep inside your ear canal send messages to your brain to help process how your body is moving. Are you traveling in a car? Are you moving up and down, in an elevator on an escalator? Your brain quickly and automatically sends signals to your muscles to help you keep your balance in any environment. An infection or issue with your inner ear disrupts those signals, which can lead to balance disorders. If you are experiencing dizziness or having any issues with your balance, contact your doctor immediately. They’ll test your earing and examine your ears and may recommend additional tests to help determine the cause of the problem.
The human ear NEVER stops working! Our ears are processing sounds even when we are asleep, but our brain just chooses to ignore sounds and vibrations. It even decides when to ignore noisy outside sounds but will still wake your promptly when your alarm clock starts beeping! You might be sleeping, or even unconscious, but your ears are always operational.
All of us have heard the story: if you hold a seashell up to your ear, even miles away from the beach, you’ll hear the sound of ocean waves crashing on a beach. It may be disappointing, but some scientists say that the sound you are really hearing is most likely the echo of the blood pumping through the blood in your own head. Other experts disagree and say that the most likely answer is the echo of the noise in the air around you. The spirals in the seashell capture the ambient noise, which resonates inside the shell and reenters your ear. Either way, it’s definitely not the sound of vacations past!
Up to 10% of skin cancers occur on the outer ears. The thin skin is very sensitive, and likely to be exposed to direct sunlight as you go about your day-to-day activities. Apply a high-SPF sunscreen to the tops and sides of your ears and flip them forward to completely cover the area behind them. A hat can also offer additional protection. If you experience any pain, spot any flaky patches or spots, feel any lumps, or see any redness, contact a medical professional immediately. Hearing loss can affect people of any age. In fact, a large percentage of individuals who experience issues with their hearing are under the age of 65. If you are experiencing any symptoms or issues with your ears or hearing, contact a professional immediately. Early intervention and treatment can go a long way in mitigating any permanent damage or hearing loss. Click here to book an appointment with our specialist now!
The human body is a bilateral structure, which means that the left and right sides are symmetrical to each other, and we have two of everything – two eyes, two hands, and so on.
Having two ears help us differentiate where the sound is coming from. When sound waves reach our ears, they arrive at our left and right ear with a difference of fractions of a second. This microscopic delay is used by our brains to determine from which direction the sounds came from!
Sounds that are impossible to hear!
The human ear has a frequency range of about 20 to 20,000 Hz. The upper limit is the cut-off point for hearing high frequencies, while the lower limit is the cut-off point for hearing low frequencies. This means that we cannot hear sounds with frequencies below 20 or above 20,000 Hz because, unlike some other creatures on the planet, our bodies have not developed to interpret these frequencies. No matter how loud these sounds are, if they are out of our range, we simply cannot hear them!
The left ear is connected to the acoustic nerve, which transmits sound information to the brain. The right ear is connected to the vestibulocochlear nerve, which transmits balance and spatial orientation information from your inner ear. However, there is no real connection between the two years – they don’t form a tunnel!
Ear wax is composed of a mixture of dead skin cells, sweat, and oil. It helps prevent infection in the ear canal by trapping dirt and other particles. It also helps to regulate the ear’s temperature by acting as a natural insulator.
Last updated : September 2022
Tags: Hearing Health

Hearing is so essential to how we engage with the people and activities
By: admin | November 28, 2024

Have you ever considered the effects of the sun on your ear health?
By: admin | July 24, 2024

Healthcare is changing, and with the rise of telehealth, so is hearing
By: admin | May 31, 2024
